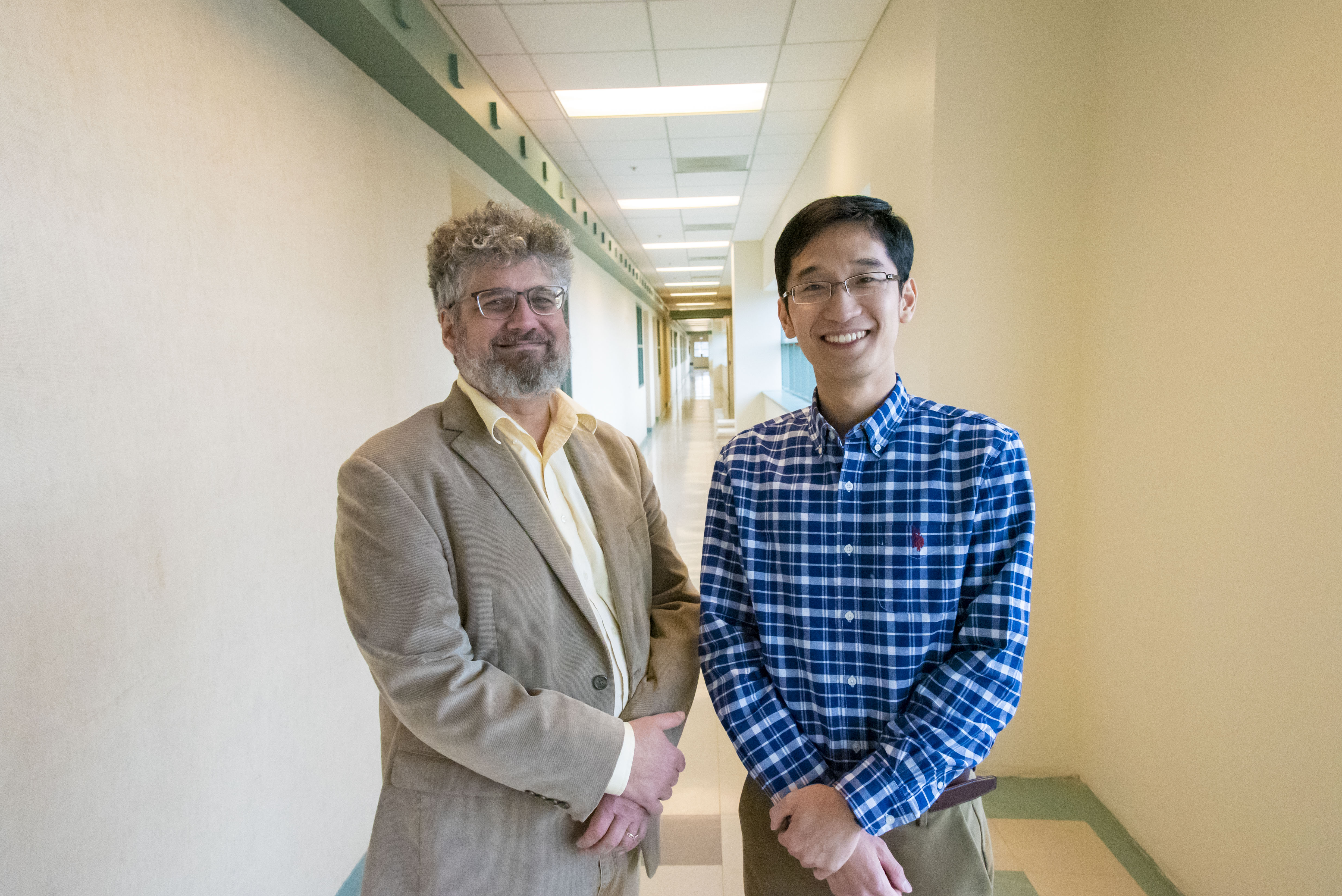
A reporter's PressPass is required to access this story until the embargo expires on 18-Apr-2024 10:00 AM EDT The Newswise PressPass gives verified journalists access to embargoed stories. Please log in to complete a presspass application. If you have not yet registered, please Register. When you fill out the registration form, please identify yourself as a reporter in order to advance to the presspass application form.
access_time Embargo lifts in 2 days
This news release is embargoed until 18-Apr-2024 10:00 AM EDT
Released to reporters: 12-Apr-2024 1:05 PM EDT










20240326113011.png&width=400&height=400)