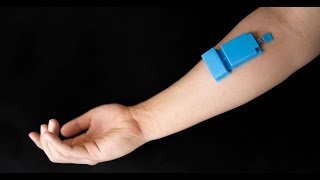
Wearable Ultrasound Tech for Muscle Monitoring Opens New Possibilities in Healthcare and Human-Machine Interfaces
University of California San DiegoResearchers have developed a compact, wearable ultrasound device that monitors muscle activity. Attachable to the skin with an adhesive and powered by a small battery, the device wirelessly captures high-resolution images of muscle movements, enabling continuous, long-term monitoring. When worn on the rib cage, it effectively monitored diaphragm function for respiratory health assessments. When worn on the forearm, it accurately captured hand gestures, allowing users to control a robotic arm and even navigate virtual games. This new technology has potential applications in healthcare for conditions affecting muscle function, as well as in human-machine interfaces for more natural robotic control.